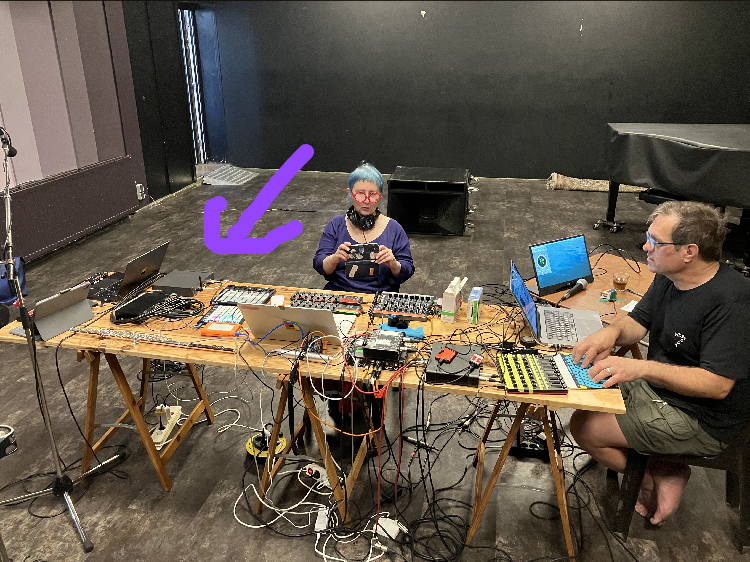
Data sonification, often used for outreach, education and accessibility, is also an effective tool for scientific exploration and discovery!
Working from the Lindorff-Larsen et al Science (2011) atomic-level molecular dynamics simulation of multiple folding and unfolding events in the WW domain, we heard (and analytically confirmed) correlations between hydrogen bond dynamics and the speed of a protein (un)folding transition.
The results were published this week in The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), vol. 121 no. 22, 28 May 2024: “Hydrogen bonding heterogeneity correlates with protein folding transition state passage time as revealed by data sonification”
Congratulations to everyone in the Biophysics Sonification Group:
Carla Scaletti (1), Premila P. Samuel Russell (2), Kurt J. Hebel (1), Meredith M. Rickard (2), Mayank Boob (2), Franz Danksagmüller (9), Stephen A. Taylor (7), Taras V. Pogorelov (2,3,4,5,6), and Martin Gruebele (2,3,5,8)
(1) Symbolic Sound Corporation, Champaign, IL 61820, United States;
(2) Department of Chemistry, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, IL 61801, United States;
(3) Center for Biophysics and Quantitative Biology, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, IL 61801, United States;
(4) School of Chemical Sciences, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, IL 61801, United States;
(5) Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, IL 61801, United States;
(6) National Center for Supercomputer Applications, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, IL 61801, United States;
(7) School of Music, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, IL 61801, United States;
(8) Department of Physics, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, IL 61801, United States;
(9) Musikhochschule Lübeck, 23552 Lübeck, Germany